Full Text Searchable PDF User Manual
1
Overview
The P5GX-M mainboard complies with the specifications for a microATX
motherboard. MicroATX boards are no larger than 9.6” x 9.6” (244mm x 244mm).
This mainboard measures 9.6” x 7.75” (244mm x 197mm).The MicroATX
specification reduces system cost by utilizing a reduced chassis with a smaller power
supply. Increased motherboard integration reduces the demand for expansion slots.
The microATX form factor permits reduced case sizes and smaller power supply units.
However, the board can also be used in standard ATX cases if required.
The P5GX-M mainboard is designed around the Cyrix GXm processor. The Cyrix
GXm CPU is an Pentium-MMX compatible processor which reduces system cost by
integrating audio and video functions into the CPU and chipset. The system also
supports a PCI IDE interface, up to 256 MB of SDRAM, and a full set of I/O ports.
The P5GX-M is an excellent low-cost platform for inexpensive multimedia
workstations or an entry-level stand-alone computer. It requires just a processor and
memory module to be fully functional.
Features
Pentium-MMX Performance
The key feature of the P5GX-M mainboard is the support for the Cyrix GXm
processor. This board can run Cyrix GXm CPUs with clock speeds of 200, 233, and
266 MHz. The processor includes a 16K block of level-1 cache memory for enhanced
performance.
Highly Integrated Support Chipset
The Cyrix GXm processor is supported by the CX5530 companion chip. This chip
provides the system logic for a Pentium MMX-compatible mainboard. It supports PCI
IDE channels with bus mastering, power management, PCI to ISA bridge, and USB
ports. In addition, the CX5530 includes an integrated graphics sub-system with MPEG
acceleration, and an integrated 16-bit audio sub-system compatible with the Sound
Blaster standard.
SDRAM Memory Support
The mainboard includes two sockets for the installation of 168-pin, 3.3V SDRAM
memory modules. Each socket can be installed with a memory module with a
maximum capacity of 128 MB, so the maximum memory of the mainboard is 256 MB.
2
Integrated Audio & Video Sub-systems
This mainboard features fully integrated audio and video subsystems, so that after the
installation of the processor and a memory module, the system is fully functional and
ready for use. The graphics system supports the MMX multimedia instruction set and
2D graphics. The graphics system uses the Unified Memory Architecture which
eliminates the need for expensive video memory, without loss of performance, by
utilizing blocks of main memory for display memory. The audio system is 16-bit
stereo and fully compatible with the Sound Blaster standard. The audio system
includes a built-in Game/MIDI port and sound jacks for microphone, stereo-in and
stereo-out.
Four Usable Expansion Slots
The P5GX-M mainboard has four expansion slots. Two slots are 8/16-bit ISA slots
and two slots are 32-bit PCI slots. Since the mainboard has integrated video and audio
sub-systems, four expansion slots are adequate for most environments.
Full Set of I/O Ports
The mainboard is installed with the NS PC97317 Super I/O chip. This chip provides a
complete solution for the board’s I/O. The board is installed with a parallel port (Bi-
directional, ECP, EPP), two serial ports (UART 16550-compatible), a PS/2 keyboard
port and PS/2 mouse port. Optionally, one serial port can be configured as a serial port
(SIR or FIR). The I/O ports are arranged in a standard ATX two-tier array that is
supported by most ATX case I/O templates.
Programmable Firmware
The mainboard includes Award BIOS which allows BIOS setting of CPU parameters.
The fully programmable firmware enhances the system features and allows users to set
power management, hardware monitoring (optional), LAN and Modem wake up
alarms, and so on.
3
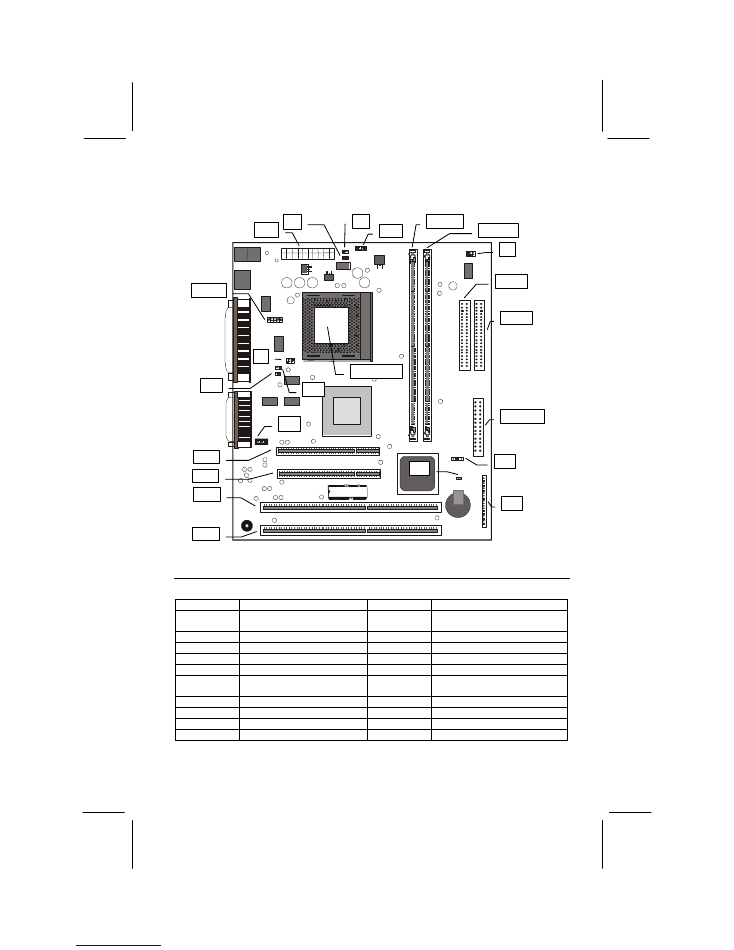
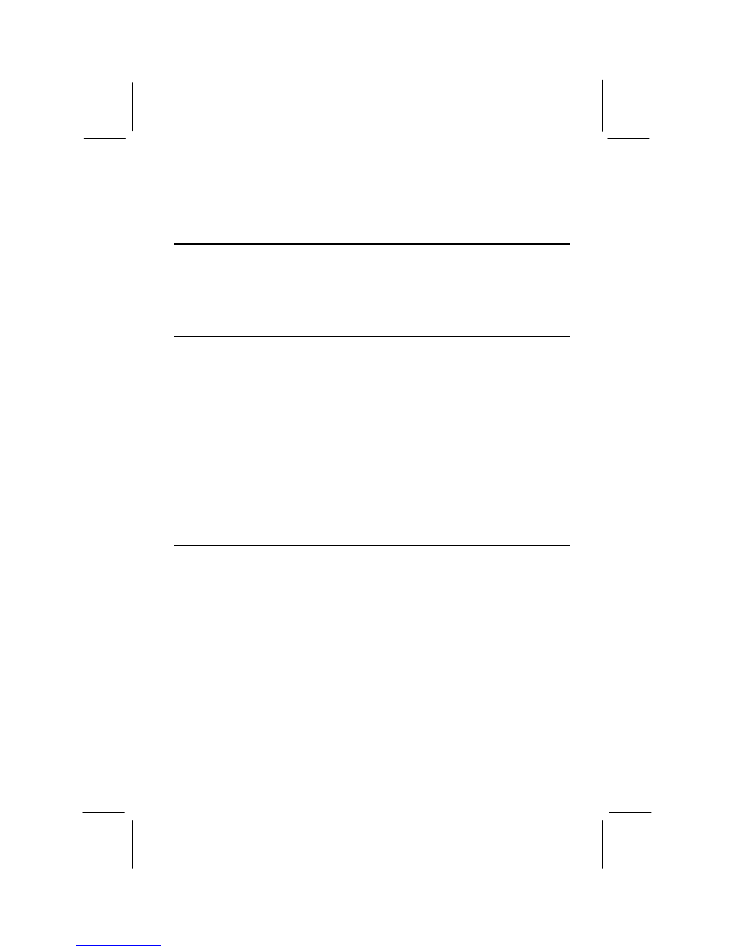
Mainboard Illustration
JP2
J4
J1
JP1
DIMM1
DIMM2
J2
CON1
CON2
FLOPPY
J17
J18
J19
ISA2
ISA1
PCI2
PCI1
J15
J11
J10
J8
SOCKET7
COM2
Key to Mainboard Components
Component
Description
Component
Description
SOCKET7
CPU Socket
(Cyrix GXm CPU only)
J4
Cooling fan power 2
DIMM1,2
Memory module sockets
JP1
CPU voltage selector
ISA1,2
8/16-bit ISA expansion slots
J2
PCI Bus speed selector
PCI1,2
32-bit PCI expansion slots
J17
SIR infrared connector
JP2
ATX power connector
J18
Clear CMOS memory jumper
COM2
Serial port COM2/4
connector
J19
Panel connector
CON1
Primary IDE connector
J15
CD-ROM audio connector
CON2
Secondary IDE connector
J10
LAN wake up connector
FLOPPY
Floppy disk drive connector
J11
Modem wake up connector
J1
Cooling fan power 1
J8
CPU clock speed selector
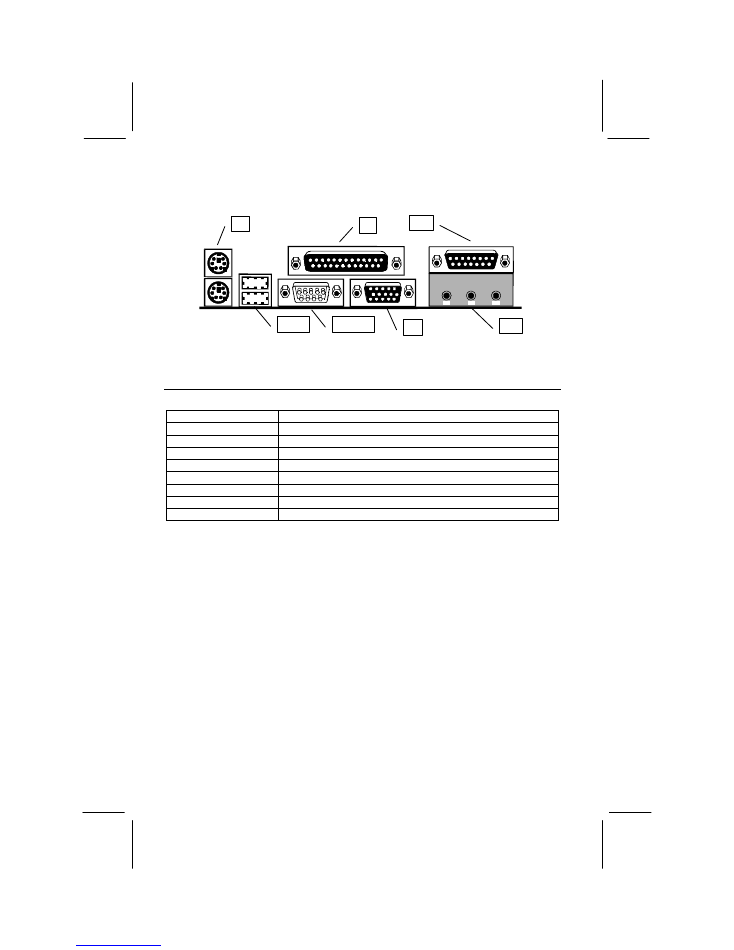
4
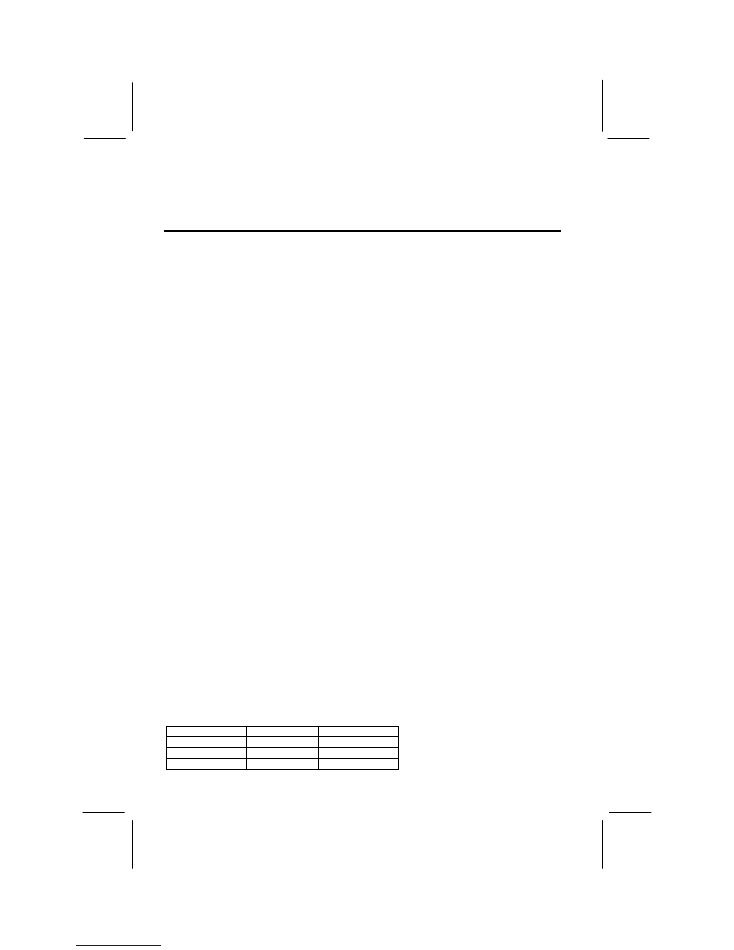
I/O Port Array Illustration
J3
USB1
JCOM1
J9
J12
J7
J12
Key to I/O Port Components
Component
Description
J3 (Upper)
PS/2 port for PS/2 mouse or pointing device
J3 (Lower)
PS/2 port for PS/2 keyboard
J7
Parallel Port (Bi-directional, EPP, ECP)
J12 (Upper)
Game/MIDI port for joystick or MIDI device
J12 (Lower)
Audio Jacks for Stereo Out, Stereo In, Microphone
J9
Port for display monitor
JCOM1
Serial port for COM1 or COM3
USB1
Two Universal Serial Bus ports
5
Installation Procedure
Prepare the Mainboard
Prepare the main board by installing the Cyrix GXm processor and then installing
either one or two memory modules. This board supports the 200, 233, or 266 MHz
version of the Cyrix GXm processor. Finally, use the selection jumpers to configure
the board for the correct bus and clock speeds.
Install the Processor
1.
Locate the zero insertion force (ZIF) SOCKET7 for the processor. On the socket
and on the processor, identify the pin 1 corner. You can identify the pin 1 corner
by noting that in the rectangular matrix of pins and holes on the socket and
processor, one pin and one hole is absent on the pin 1 corner.
2.
Push the socket locking lever away from the socket to unhook it. Swing the lever
into the upright position.
3.
Insert the processor into the socket taking care that you have matched the pin 1
corners. No force is required, and the processor should seat smoothly into the
socket.
4.
Swing the locking lever down and hook it under the latch on the side of the socket
to lock it in place.
5.
Locate the power connectors for cooling fans J1 and J4. Connect the cable from
the processor cooling fan to either J1 or J4.
Install the Memory Modules
For this mainboard, you must use 168-pin Dual In-line Memory Modules (DIMMs)
which are installed with SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory)
(SDRAM). This mainboard supports 3.3 volt DRAMs. This board can operate with a
30, 33 (Default) MHz system bus.
You can install 1 or 2 modules. If you only install one memory module, install it in
DIMM socket 1, and if you install two modules, install them in DIMM sockets 1 and 2.
Each module can have a maximum capacity of 128 MB, so you can install a maximum
of 256 MB using two modules.
1.
The SDRAM sockets are keyed with notches and the DIMMs are keyed with cut-
outs so that they can only be installed correctly. Check that the cut-outs on the
DIMM edge connector matches the notches in the SDRAM socket.
2.
Push the latches on each side of the SDRAM socket down.
3.
Install the edge connector of the DIMM into the socket and press it carefully but
firmly down so that it seats correctly. The latches at either side of the socket will
6
be levered upwards and latch on the edges of the DIMM when it is installed
correctly.
Check the Jumper Settings
Use the mainboard selection jumpers to configure your board for the correct clock
speed, voltage, and bus timing according to the CPU that you have installed. Set other
selection jumpers to the correct settings.
CPU Setting
To install a CPU on this mainboard you need to set up the board for a specific CPU by
doing the following:
q
Set the External Clock Speed
q
Set the Clock Multiplier Factor
q
Set the CPU Voltage
You configure the CPU settings using the jumpers on the mainboard. In order to do
this, you will need to know some information about the CPU you plan to use. This
should be provided by the CPU vendor. You’ll need the following information:
q
CPU Internal Clock Speed
q
CPU Voltage
The internal clock speed is the speed the CPU operates at to process data and is the
one used by CPU manufacturers to indicate the speed of the chip. The CPU also has an
external clock speed which is the speed at which it interacts with the external
components.
CPU voltage may either be the same internally and externally or it may be split,
depending on the CPU design. Some processors use one voltage for the core (Vcore)
and another for input/output (Vio).
To configure the board for a CPU’s internal clock speed, you need to set the external
clock speed, sometimes referred to as the bus speed, and the clock multiplier, so that
the result is the internal clock speed of the CPU you are installing.
For example, the default setting for these is:
33 MHz (External Clock) x 6 (Clock Multiplier) = 200MHz
or an effective setting of 200MHz
Check the table below to find the default settings for the CPU’s used by this
motherboard.
CPU Type
PCI Speed
Clock Multiplier
GXm 200
33
6X
GXm 233
33
7X
GXm 266
33
8X
7
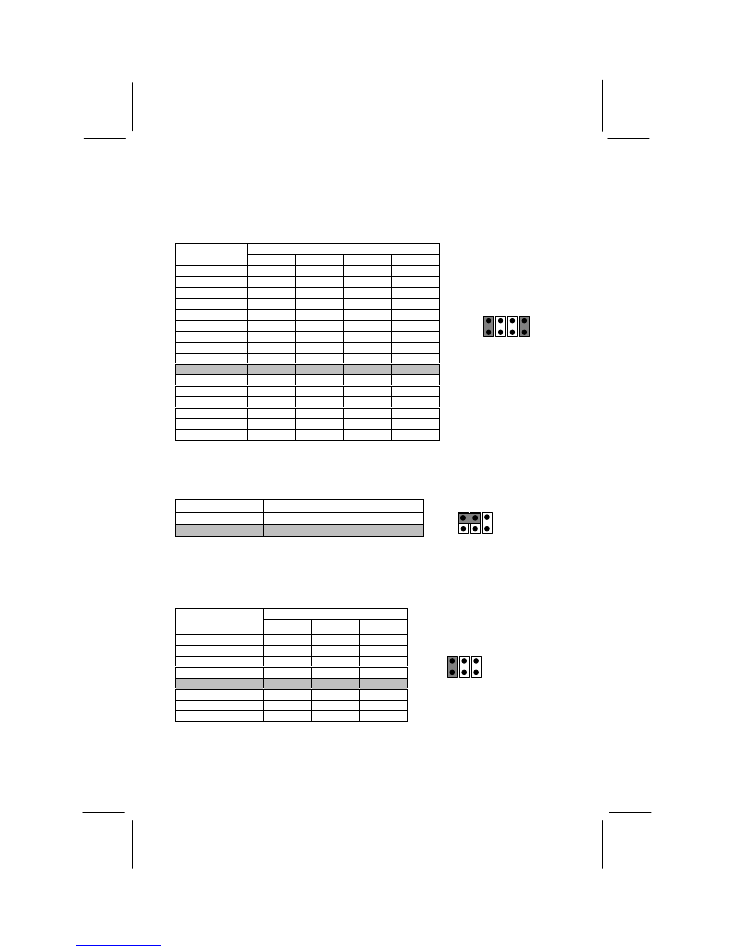
JP1: Set CPU Voltage Jumper
JP1 consists of four 2-pin jumpers. Use the jumpers to set the core voltage for the
processor. See the processor documentation for information on which voltage your
processor requires.
Jumper Settings
Processor
Core Voltage
Pins 1-2
Pins 3-4
Pins 5-6
Pins 7-8
Shutdown
Open
Open
Open
Open
2.1V
Short
Open
Open
Open
2.2V
Open
Short
Open
Open
2.3V
Short
Short
Open
Open
2.4V
Open
Open
Short
Open
2.5V
Short
Open
Short
Open
2.6V
Open
Short
Short
Open
2.7V
Short
Short
Short
Open
2.8V
Open
Open
Open
Short
2.9V
Short
Open
Open
Short
3.0V
Open
Short
Open
Short
3.1V
Short
Short
Open
Short
3.2V
Open
Open
Short
Short
3.3V
Short
Open
Short
Short
3.4V
Open
Short
Short
Short
3.5V
Short
Short
Short
Short
J2: Set PCI Bus Speed Jumper
J2 consists of three 2-pin jumpers. Use the jumpers to set the speed of the PCI bus.
PCI Bus Speed
Short Pins
30 MHz
4-6
33 MHz
2-4
J8: Set CPU Clock Speed Jumper
J8 is a set of three 2-pin jumpers. J8 defines a multiplier. The multiplier times the
system bus speed produces the clock speed for the processor.
Jumper Cap Setting
Bus Speed
Multiplier
Pins 1-2
Pins 3-4
Pins 5-6
X10
Short
Open
Short
X9
Open
Short
Short
X8
Open
Open
Open
X7
Open
Short
Open
X6
Short
Open
Open
X5
Open
Open
Short
X4 (Testing only)
Short
Short
Short
Reserved
2
1
8
7
Default 2.9V
JP1
2
1
6
5
Default
X6
J8
2
1
6
5
Default
J2
8
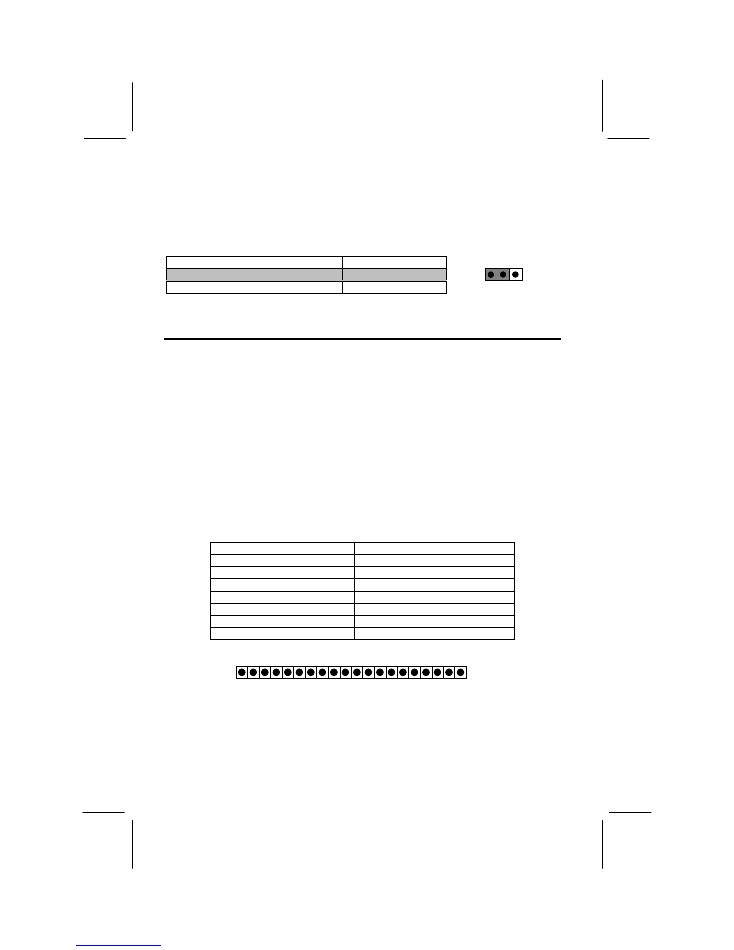
J18: Clear CMOS Memory Jumper
If you ever need to clear the system CMOS memory, you can do this by moving the
jumper cap to short pins 2-3 for a few seconds. When you clear the CMOS memory,
the system must be turned off and the ATX power supply cable disconnected from the
ATX power connector on the motherboard.
Function
Jumper Position
Normal Operation
Short pins 1-2
Clear CMOS Memory
Short pins 2-3
Make the Internal Connections
1.
Locate the floppy diskette drive connector FLOPPY. Use the ribbon cable to
connect the floppy diskette drive to the mainboard.
2.
Locate the Enhanced IDE connectors CON11 (primary) and CON2 (secondary).
A single IDE cable is provided with the mainboard. Connect the cable to CON1
The cable has two connectors for IDE devices. If you connect two devices, you
must configure one device as Master, and one device as Slave. See the
documentation provided with the devices for information on this. If you need to
install more drives, obtain another IDE cable and connect one or two devices to
CON2 following the same procedure as you used with CON1.
3.
Locate the bank of switch and indicator connectors J19. These connectors provide
control functions to your system case. Use the illustration below and the following
table to make the connections.
Function
Pinout
Power Indicator
+1, +2, 3
Sleep Switch
4, 5
Suspend Indicator
+6, +7, 8
Reset Switch
9, 10
Speaker
+13, 14, 15, 16
Hard Disk Indicator
+17, 18
Power Switch
19, 20
4.
Locate the ATX power connector JP2. Connect the cable from your system ATX
power supply into the connector. The connector is keyed so that it can only be
installed correctly.
1 2 3
Default
J18
Power
SW
3 1
5 4
8 6
16 13
10 9
18 17
20 19
HDD
LED
Speaker
Reset
SW
Suspend
LED
Sleep
SW
Power
LED
9
Make the Optional Internal Connections
1.
Install any expansion cards into the expansion slots. The system has two 32-bit
PCI slots (PCI1, 2) and two 8/16-bit ISA slots (ISA1, 2).
2.
If you have installed an internal fax/modem, cable the fax/modem to the modem
wake up connector J11. This will allow the system to wake up from a power
saving mode when an incoming call is detected.
3.
If you have installed an internal network adapter, cable the adapter to the LAN
wake up connector J10. This will allow the system to wake up from a power
saving mode when incoming network traffic is detected.
4.
If you have installed a CD-ROM drive, connect the audio-out cable from the CD-
ROM drive to the CD-Audio connector J15 on the mainboard.
5.
If you are installing an optional infrared port, connect the cable from the infrared
port to the mainboard infrared connector, J17 (SIR-Serial Infrared).
6.
If you are installing an optional second serial port, connect the cable from the
second serial port to the mainboard serial port connector COM2.
Note: If you install an infrared port, it must share a COM port assignment with
the second external serial port COM2. If you have installed a second serial
port and an infrared port, select which port is in use by using the setup utility.
7.
If your system case has a chassis-mounted cooling fan, connect the cable from the
fan to one of mainboard cooling fan power supplies J1 or J4.
10
System BIOS
The system is installed with a programmable Award BIOS. The BIOS is stored on an
erasable EEPROM so that updated BIOS can be flashed to the system using the flash
BIOS utility in system software.
The BIOS allows system integrators to set processor and timing parameters for
maximum performance or maximum stability. It allows end users to set power
management routines and install password protection.
The BIOS setup utility can be started by pressing the Delete key, shortly after the
system has been powered on. A prompt appears on the screen telling you to do this.
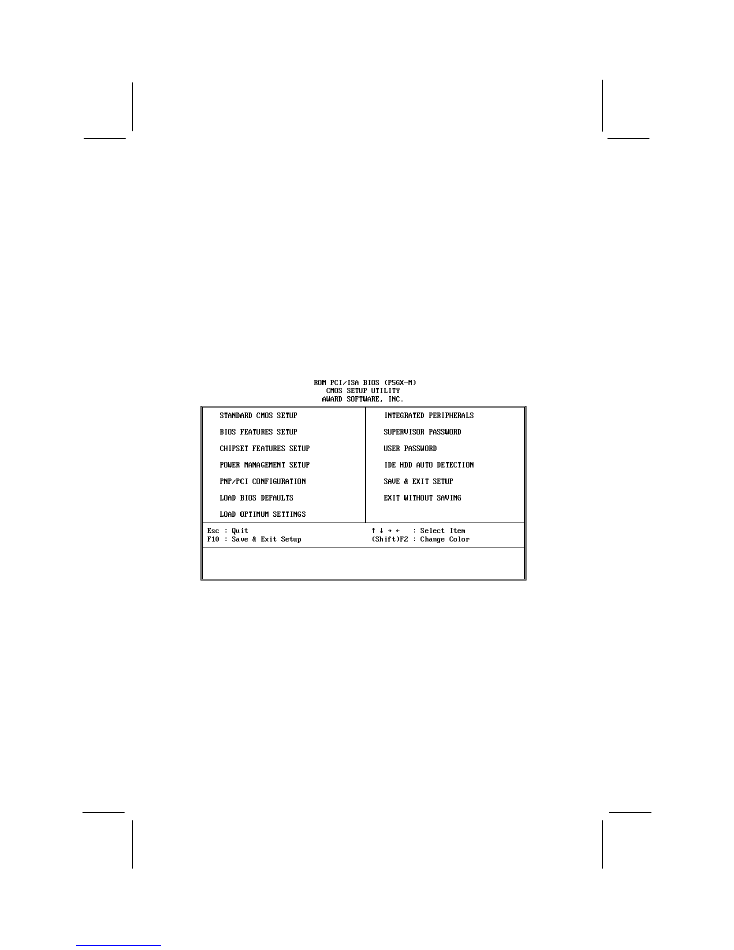
When the setup utility starts, a main menu appears which shows the main features of
the setup utility.
Standard CMOS Setup
This option sets basic information about the system such as the date and time, the disk
drives, and the memory.
BIOS Features Setup
This option sets more advanced information about the system such as processor clock
and system bus, the boot sequence, virus protection, and so on.
Chipset Features Setup
This option displays advanced information about system timing parameters. System
integrators can use this option to troubleshoot the system, and configure hardware for
performance or reliability.
11
Power Management Setup
This option lets users set power management timeouts for the system and install
features such as LAN wake up, modem wake up, and so on.
PNP/PCI Configuration
This option configures assigns Plug and Play control to either the BIOS or the OS (if
supported). It allows older (legacy) ISA cards to be configured manually.
Load BIOS Defaults
This option loads all of the setup utility with an undemanding set of defaults which
should work with most hardware configurations.
Load Optimum Settings
This option loads all of the setup utility with a high-performance set of defaults which
should work with the recommended hardware configurations for this system.
Integrated Peripherals
This option lets users and system integrators configure parameters for disk drives, I/O
ports, and so on. Port addresses and interrupt request lines can be set.
Supervisor Password and User Password
These options allow users and system integrators to install Supervisor and User
password protection to either system start up or entry to the system setup utility.
IDE Auto Detection
This option provides automatic detection and configuration for most modern IDE hard
disk drives.
Save & Exit Setup and Exit Without Saving
These two items allow changes to the system setup utility to be saved or discarded.
12
System Software
The support software for this mainboard is supplied on either a CD-ROM disk, or a
floppy diskette, depending on the configuration of the mainboard. Some mainboard
configurations do not need all the software described in this chapter.
♦
Bus master IDE driver
Please notice that the support software for this mainboard is supplied without
IDE Bus Master Driver for the time being. Thus, this board can not run IDE
Driver under the Bus Master Mode and it can not support Ultra DMA33
neither. The chipset vendor Cyrix just provide us IDE Driver beta version at
this stage, we will provide the complete IDE Bus Master Driver in the next
version.
♦
Audio driver
♦
Graphics driver
♦
PCI Bridge Driver
Installing the Audio Driver
1.
Go to the System Properties window (Start/Settings/Control Panel/system).
2.
Click on the Device Manager tab and select the "View Devices by type" radio
button.
3.
Under System Devices, make sure to remove the items "Unknown Device" and
"PCI Multimedia Audio Device" on the "? Other devices"
4.
Close the System Properties window.
5.
Go to the Add New Hardware window (Start/Settings/Control Panel/).
6.
When the wizard pops up to help you install new hardware, click next once. In the
next window, select "No", you do not want Windows to help you search for new
hardware. Click Next to proceed.
7.
In the next window, select Sound, Video and Game Controllers when asked to
pick the type of hardware you want to install. Click Next to proceed.
8.
In the next window, click the Have Disk button. The program then prompts you to
type a path name where it can find the proper driver. The Sound Driver can be
found in the a:\audio\win95 directory of the disk provided.
9.
The program will then list all the drivers available on that disk, make sure to pick
"Cyrix Corporation" and "XpressAUDIO (TM) 16-bit Sound". Proceed and
follow the directions onscreen.
Installing the Graphics Driver
1.
Close all programs.
2.
Go to the Display Properties window (Start/Settings/Control Panel/).
3.
Click on the Settings.
4.
Click on the Advanced Properties button.
5.
On the Adapter window, click on the Change button.
13
6.
In the next window, click the Have Disk button. The program then prompts you to
type a path name where it can find the proper driver. The Graphics Driver can be
found in the a:\vga\win95 directory of the disk provided.
7.
The program will then list all the drivers available on that disk. Pick the
appropriate driver from the list. Proceed and follow the directions onscreen.
8.
After successfully installing the graphics driver, you need to restart the system for
the new drivers to take effect.
PCI Bridge Driver
Since Windows 95/98 doesn't provide support for NS5530 I/O chipset, it will
recognize the "PCI Bridge" as an "Unknow Device". We offer "PCI Bridge Driver"
to solve this issue, please follow the instructions below :
1.
Go to the "Control Panel/System".
2.
Go to Device Manager and pick up "Unknow Device/PCI Bridge".
3.
Click "Content/Driver/Update driver".
4.
When the Winzard pop up, select the file a:\5530\5530.inf to install driver.